education
- by piwi215
- 5 posts
-
The London School of Economics (LSE) will be offering an online course on cryptocurrencyinvesting, starting in August 2018, Financial Times reports Monday, July 9.
According to the announcement, the new course dubbed “Cryptocurrency Investment and Disruption,” will help students learn some “practical skills to interact with cryptocurrency exchanges,” including how to use cryptocurrency wallets, as well as “evaluate the analytics” of initial coin offerings (ICOs).
The LSE, which is alma mater to 36 “world leaders” and 18 Nobel Prize laureates, claims it is known for its motto to “understand the causes of things.” By introducing the course, the university intends to help global “private organisations, individual investors, financial service firms, governments,” as well as “regulatory bodies” to make sense of the “highly disruptive trend” of crypto.“The exponential growth and volatility of cryptocurrencies and the distributed ledger technology underpinning them has led to a global interest in cryptoassets, ICOs and the distribution of digital wealth.”
The online course is set to be led by Dr Carsten Sørensen, Associate Professor of Information Systems and Innovation. Consisting of six modules that add up to 60 hours of class time, participation in the course will cost €1,800, or roughly $2,116.
The University of Malta was also reported today to announce a blockchain degree that will be taught starting in October 2018.In February, Australian public research university RMIT launched the country’s first university course on blockchain technology.
The 8-week course, dubbed “Developing Blockchain Strategy”, intends to teach not only theoretical aspects of blockchain, but also the practical skills needed to use the technology.-
- 1
Francisco Gimeno - BC Analyst LSE is one of the most influential School of economics in the world. The title of their new course "Cryptocurrency Investment and Disruption" show that they really want to provoke understanding of what is coming, and why, and its consequences.- 10 1 vote
- Reply
-
-
- Blockchain is "definitely an opportunity" in the long term, says UBS Group CEO Sergio Ermotti.
- He says it is a great way to reduce costs.
- "Our industry will continue to be under pressure, in terms of gross margins. It's no doubt," he says.
Michelle Fox
UBS CEO: Blockchain technology almost a must-have 10 Hours Ago | 01:04
Swiss financial services giant UBS Group may not be a fan of bitcoin but CEO Sergio Ermotti believes blockchain, the technology behind cryptocurrencies, is "definitely an opportunity" in the long term."It's almost a must.
The freeing up of resources to become more efficient will come through technology and blockchain is a great way to allow us to … reduce costs," Ermotti told CNBC's Michelle Caruso-Cabrera on Monday.
Blockchain allows data to be stored across a network of computers around the world rather than at one single location.
"Our industry will continue to be under pressure, in terms of gross margins. It's no doubt," he said. "The only way you can stay relevant is not only by being strong in terms of capital, in terms of products, the quality of the people you have, advice you give to clients. You need also to be able to price it correctly."
UBS is currently involved in a blockchain-based global trade finance platform, called Batavia, along with IBM and other banks. Ermotti said the focus is on the future, noting that transforming the cost base of the industry won't happen "tomorrow."
Instead, he's looking five to 10 years out.He's convinced that the technology "will be as crucial and disruptive, and changing as regulation was in the last 10 years."
However, Ermotti still hasn't come around on bitcoin. He's already said he is "not necessarily" a believer in cryptocurrencies. Last October, UBS warned bitcoin was in a "speculative bubble."
UBS CEO: Many assets are expensive 15 Hours Ago | 04:47Trade war concerns
Ermotti also spoke with CNBC on Monday about the possibility of a trade war between the U.S. and China."I'm really worried that ... these things are going to get out of control. Somebody is going to announce something that then triggers a more serious issue," he said, stressing trade risk "could come from any side, Europe, U.S., China; you name it."
— CNBC's Ryan Browne and Matt Belvedere contributed to this report.
Michelle Fox-
Francisco Gimeno - BC Analyst Financial institutions supporting Blockchain as the technology to adopt to save on costs, speed and get a more trustful and transparent environment are coming out every day. They are yet unhappy about cryptos, but they know what the future is, the 4th Industrial revolution.
-
Though the availability of formal cryptocurrency and blockchain education around the globe is increasing rapidly, the UK Department for Education (DfE) appear to have no immediate plans to include cryptocurrency as a topic in the UK school curriculum.
However, the country’s school children will see a “rigorous” new mathematics curriculum and financial literacy education.
In a recent interview, a Department for Education (DfE) spokesperson did not voice any objection to cryptocurrency but equally did not indicate any plans to add the topic to the financial literacy curriculum element within UK schools.The DfE did reveal improvements to the UK curriculum that may provide important basic skills to young people with an interest in the sector:We have introduced a rigorous new mathematics curriculum and made financial literacy compulsory for 11 to 16 year olds. […] In addition, our new computing curriculum ensures pupils will have the broader knowledge and skills they need to go on to specialise in cutting edge technologies and become actively involved in using and creating their own digital technology.”
The Express also spoke to the CEO of Mandala Exchange who stressed the importance of putting more emphasis on coding in the school system:With the current push towards integrating the fundamental programming languages into school systems, blockchain should become a complimentary area of study with the possibility to major in it or specialise.
While the UK has no immediate plans to introduce blockchain and cryptocurrency into its schools, other countries are seeing the value and acting accordingly.
Earlier this year, Timothy Breza, a history and financial literacy teacher at Union Catholic Regional High School in Scotch Plains, New Jersey confirmed to CNBC the addition of cryptocurrency to his Business and Personal Finance Course for 16 to 18-year olds.
INCLUSION AT UNIVERSITY LEVEL GLOBALLY
University level courses and degrees are now available globally including at the University of California, Pennsylvania, New York, and Stanford. In 2016 the UK’s Cambridge University became the first add blockchain to its Masters in Finance degree. The University of Nicosia, Cyprus, became the first to launch an MSc Degree in Digital Currency.
A small team of Oxford University, UK, professors are looking to establish the first-ever blockchain-based university and are seeking authorization from the EU to grant degrees.
Woolf Development’s university will use distributed ledger technology and SMART contracts to provide and administer courses and certificates.
The Open University, the University of Nicosia, and the MIT Media Lab have also all explored blockchain-based administrative and certification systems.
As blockchain and cryptocurrencies infiltrate global financial infrastructures, educational systems, and many other industrial and economic sectors, should they now be included as topics in school level education?
http://bitcoinist.com/uk-department-education-says-no-cryptocurrency-curriculum-schools/
-
By
 Admin
Admin - 0 comments
- 3 likes
- Like
- Share
-
By
-
Bitcoin and Blockchain-related jobs are becoming increasingly popular today. That’s why the issue of a relevant education is becoming a topic of interest as well.
No one would argue that bitcoin and blockchain are becoming more and more widespread today.
There are new solutions, new fields and new inventions applying the technology, and thereby, creating the need for professional developers, market specialists and many others. As the industry is quite young, there has been a lack of experienced and educated specialists in the field, as it was simply impossible to obtain the relevant education anywhere.
The leading cryptocurrency and blockchain professionals known to us at present are self-educated, driven by passion and enthusiasm for their work.Education is not a Problem, but What is it Needed For?
Over the course of time, leading education establishments of the world have realised the need for blockchain and cryptocurrency related courses, so now it is not so difficult to obtain an education and become a real professional in the sphere.
For example, you may study at Princeton University, Duke University,Stanford University,Berkley, The University of Cumbria, IT University of Copenhagen, B9lab Academy etc. This list is far from exhaustive.
There is even the Blockchain Academy - a specialized education establishment based in Cape Town providing both full-time and online education on blockchain technology. As we may see, there is no problem in obtaining an education at a credible university, which would make you a credible specialist at once, but what is the use of such education.
For it is not enough to get a certificate, you would need to get a job to earn your living.
Fortunately, job offers are plenty to provide enough choice. A fresh blockchain specialist may get a job at Blockchain startups and consortiums, large tech firms, banks and other private sector firms, professional services firms or even the government. They seek blockchain developers, research analysts, consultants, product managers and many other specialists.
The salaries vary considerably. In the UK, a blockchain specialist may earn £40-60k. Large companies are willing to pay £100,000 - £150,000 to the experienced professional. In Russia, an expertise in cryptocurrency or blockchain may raise your wages by 25% from the average rate.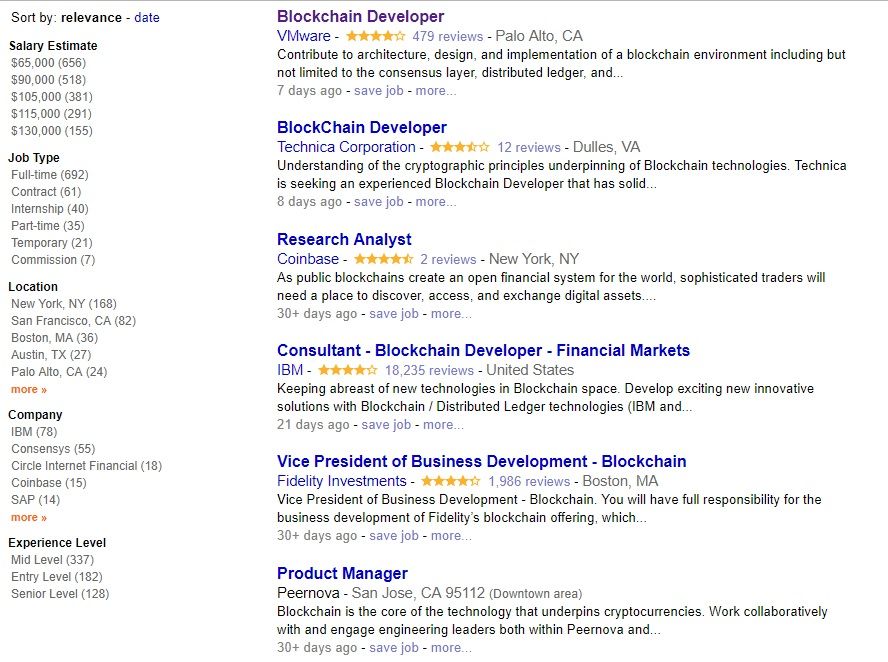
A Recipe from Ian Balina
The education opportunities are plenty. However, one may become a blockchain or cryptocurrency specialist without a university. All you need is the desire to learn. Ian Balina, a cryptocurrency investor, serial entrepreneur, author, and filmmaker, has his own recipe of how to become an expert, which he shared at Quora:- Read up on Bitcoin and Blockchain Wikipedia articles
- Read a book on Bitcoin and Blockchain; I highly recommend “Digital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent Money” by Nathaniel Popper
- Invest in Bitcoin and altcoins and actively follow them
- Every month, attend at least one local meetup or event on Bitcoin and Blockchain in your area and network with the community
- Join a Bitcoin/Blockchain related project
a. If you’re looking to become a technical expert, then definitely look at the open source code and become a contributor
b. If you’re looking to be a non-technical expert, become a writer or blogger on Bitcoin and Blockchain related topics - Attend large annual Bitcoin and Blockchain conferences
- Repeat steps 3 through 6 for at least two years, and then you will be credible enough to be a Bitcoin and Blockchain expert.
- Once an expert, you could do the following:
a. Start your own Bitcoin or Blockchain related startup
b. Start a consulting or software company on Bitcoin or Blockchain
c. Write a book on Bitcoin or Blockchain
It is up to you to choose your way of becoming a blockchain or cryptocurrency expert, for no one will argue the industry brings many opportunities and prospects.
However, no education will help you gain true expertise if you have no passion and enthusiasm for what you do.
How did you become a bitcoin and blockchain expert? Feel free to share your personal story of success in the comments below!
Have you benefitted from reading this article? Then discover even more on Coinidol here to keep up: https://coinidol.com/become-blockchain-specialist-and-where-profession-required/
-
Francisco Gimeno - BC Analyst The recipe stated in the article forgot Blockchaincompany.info! This platform is awesome for those who want to be experts on Blockchain and Crypto. The author is right somehow that by now any person who is interested and move along some parameters is automatically a Blockchain expert as becomes a "believer" who can explain at least the non technical side of Blockchain and can lead a discussion on the importance and impact of Blockchain. On a personal side, I am already using this recipe, at least most of the points. On my way.... What about you?
-
A Beginner’s Guide to Smart Contracts One of the best things about the blockchain is that, because it is a decentralized system that exists between all permitted parties, there’s no need to pay intermediaries (Middle men) and it saves you time and conflict.
Blockchains have their problems, but they are rated, undeniably, faster, cheaper, and more secure than traditional systems, which is why banks and governments are turning to them. In 1994, Nick Szabo, a legal scholar, and cryptographer, realized that the decentralized ledger could be used for smart contracts, otherwise called self-executing contracts, blockchain contracts, or digital contracts.
In this format, contracts could be converted to computer code, stored and replicated on the system and supervised by the network of computers that run the blockchain. This would also result in ledger feedback such as transferring money and receiving the product or service.
What are Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts help you exchange money, property, shares, or anything of value in a transparent, conflict-free way while avoiding the services of a middleman.
The best way to describe smart contracts is to compare the technology to a vending machine. Ordinarily, you would go to a lawyer or a notary, pay them, and wait while you get the document. With smart contracts, you simply drop a bitcoin into the vending machine (i.e. ledger), and your escrow, driver’s license, or whatever drops into your account.
More so, smart contracts not only define the rules and penalties around an agreement in the same way that a traditional contract does, but also automatically enforce those obligations.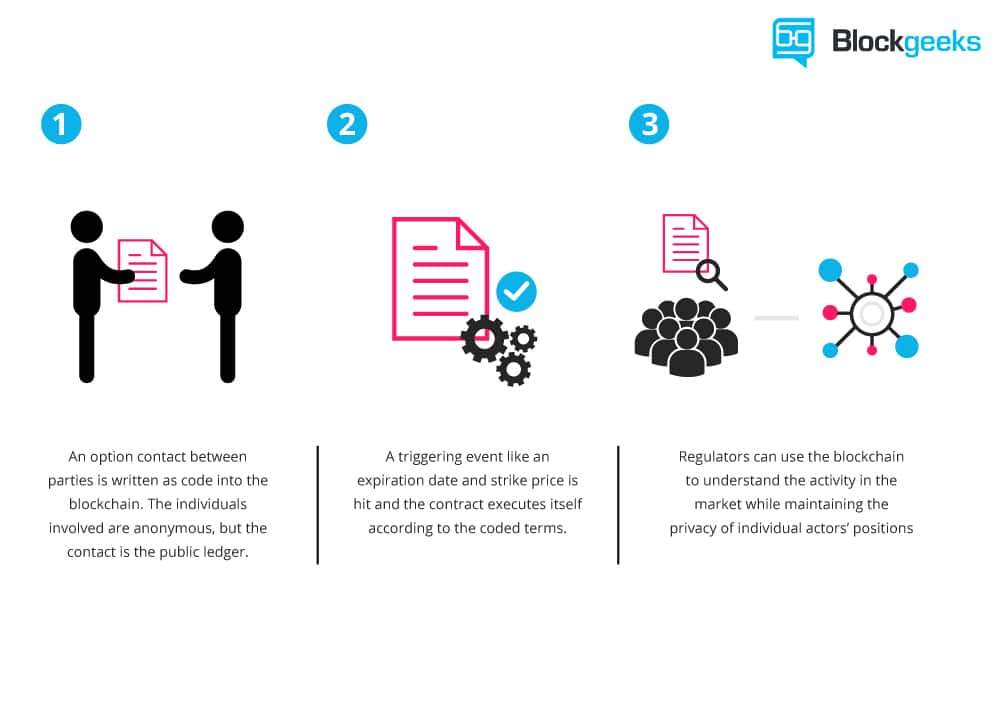

As Vitalik Buterin, the 22-year-old programmer of Ethereum, explained it at a recent DC Blockchain Summit, in a smart contract approach, an asset or currency is transferred into a program “and the program runs this code and at some point it automatically validates a condition and it automatically determines whether the asset should go to one person or back to the other person, or whether it should be immediately refunded to the person who sent it or some combination thereof.
”In the meantime, the decentralized ledger also stores and replicates the document which gives it a certain security and immutability.
Example
Suppose you rent an apartment from me. You can do this through the blockchain by paying in cryptocurrency. You get a receipt which is held in our virtual contract; I give you the digital entry key which comes to you by a specified date. If the key doesn’t come on time, the blockchain releases a refund. If I send the key before the rental date, the function holds it releasing both the fee and key to you and me respectively when the date arrives.
The system works on the If-Then premise and is witnessed by hundreds of people, so you can expect a faultless delivery. If I give you the key, I’m sure to be paid. If you send a certain amount in bitcoins, you receive the key. The document is automatically canceled after the time, and the code cannot be interfered by either of us without the other knowing, since all participants are simultaneously alerted.
You can use smart contracts for all sort of situations that range from financial derivatives to insurance premiums, breach contracts, property law, credit enforcement, financial services, legal processes and crowd funding agreements.
A Smart Contract ExampleHere is the code for a basic smart contract that was written on the Ethereum blockchain. Contracts can be encoded on any blockchain, but Ethereum is mostly used since it gives unlimited processing capability.
An example smart contract on Ethereum. Source: www.ethereum.org/token
The contract stipulates that the creator of the contract be given 10,000 BTCS (i.e. bitcoins); it allows anyone with enough balance to distribute these BTCs to others.Here’s How You Can Use Smart Contracts
 J
J
erry Cuomo, vice president for blockchain technologies at IBM, believes smart contracts can be used all across the chain from financial services to healthcare to insurance.
Here are some examples: Government Insiders vouch that it is extremely hard for our voting system to be rigged, but nonetheless, smart contracts would allay all concerns by providing an infinitely more secure system. Ledger-protected votes would need to be decoded and require excessive computing power to access.
No one has that much computing power, so it would need God to hack the system! Secondly, smart contracts could hike low voter turnout. Much of the inertia comes from a fumbling system that includes lining up, showing your identity, and completing forms. With smart contracts, volunteers can transfer voting online and millennials will turn out en masse to vote for their Potus.
ManagementThe blockchain not only provides a single ledger as a source of trust, but also shaves possible snarls in communication and workflow because of its accuracy, transparency, and automated system. Ordinarily, business operations have to endure a back-and forth, while waiting for approvals and for internal or external issues to sort themselves out.
A blockchain ledger streamlines this. It also cuts out discrepancies that typically occur with independent processing and that may lead to costly lawsuits and settlement delays. Case history In 2015, the Depository Trust & Clearing Corp. (DTCC) used a blockchain ledger to process more than $1.5 quadrillion worth of securities, representing 345 million transactions.
Supply ChainSmart contracts work on the If-Then premise so, to put
in Jeff Garzik’s words,
“UPS can execute contracts that say, ‘If I receive cash on delivery at this location in a developing, emerging market, then this other [product], many, many links up the supply chain, will trigger a supplier creating a new item since the existing item was just delivered in that developing market.’
” All too often, supply chains are hampered by a paper-based systems, where forms have to pass through numerous channels for approval, which increases exposure to loss and fraud. The blockchain nullifies this by providing a secure, accessible digital version to all parties on the chain and automates tasks and payment.
Case history
Barclays Corporate Bank uses smart contracts to log change of ownership and automatically transfer payments to other financial institutions upon arrival
Automobile
There’s no doubt that we’re progressing from slothful pre-human vertebrates to super-smart robots. Think of a future where everything is automated.
Google’s getting there with smart phones, smart glasses, and even smart cars. That’s where smart contracts helps. One example is the self-autonomous or self-parking vehicles, where smart contracts could put into play a sort of ‘oracle’ that could detect who was at fault in a crash; the sensor or the driver, as well as countless other variables.
Using smart contracts, an automobile insurance company could charge rates differently based on where, and under which, conditions customers are operating their vehicles.
Real Estate
You can get more money through smart contracts. Ordinarily, if you wanted to rent your apartment to someone, you’d need to pay a middleman such as Craigslist or a newspaper to advertise and then again you’d need to pay someone to confirm that the person paid rent and followed through. The ledger cuts your costs.
All you do is pay via bitcoin and encode your contract on the ledger. Everyone sees, and you accomplish automatic fulfillment. Brokers, real estate agents, hard money lenders, and anyone associated with the property game can profit.
Healthcare
Personal health records could be encoded and stored on the blockchain with a private key which would grant access only to specific individuals. The same strategy could be used to ensure that research is conducted via HIPAA laws (in a secure and confidential way).
Receipts of surgeries could be stored on a blockchain and automatically sent to insurance providers as proof-of-delivery. The ledger, too, could be used for general health care management, such as supervising drugs, regulation compliance, testing results, and managing healthcare supplies.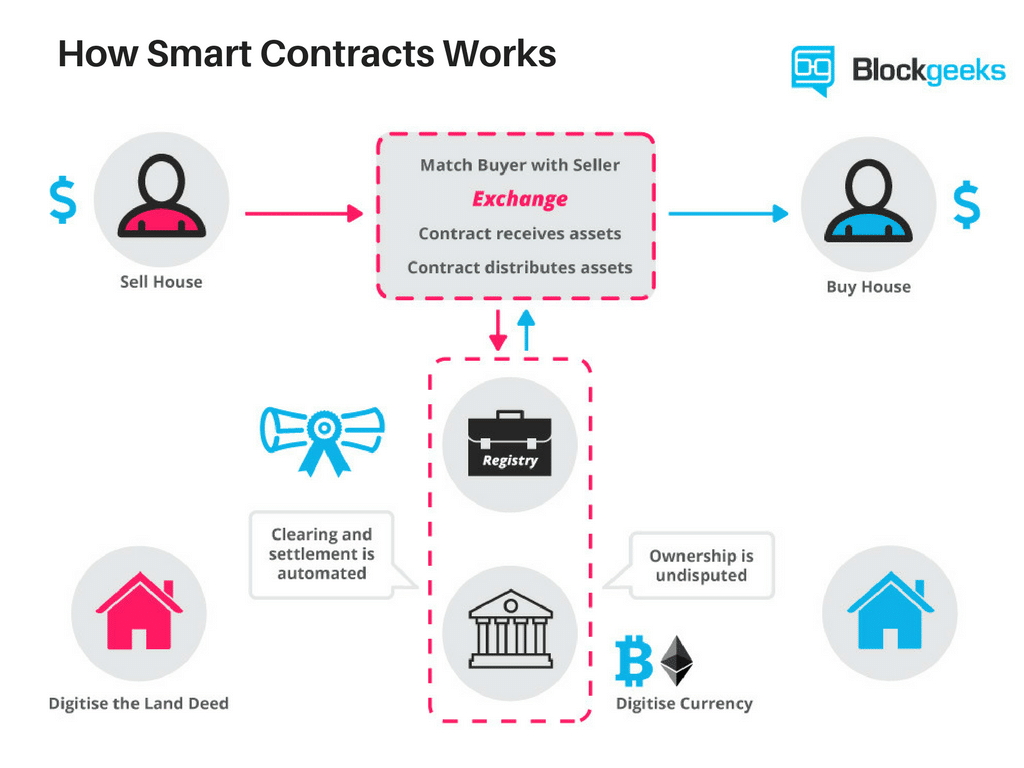
Smart Contracts are Awesome!
Here’s what smart contracts give you: Autonomy – You’re the one making the agreement; there’s no need to rely on a broker, lawyer or other intermediaries to confirm. Incidentally, this also knocks out the danger of manipulation by a third party, since execution is managed automatically by the network, rather than by one or more, possibly biased, individuals who may err.
Trust – Your documents are encrypted on a shared ledger. There’s no way that someone can say they lost it. Backup – Imagine if your bank lost your savings account. On the blockchain, each and every one of your friends has your back.
Your documents are duplicated many times over.Safety – Cryptography, the encryption of websites, keeps your documents safe. There is no hacking. In fact, it would take an abnormally smart hacker to crack the code and infiltrate.
Speed – You’d ordinarily have to spend chunks of time and paperwork to manually process documents.
Smart contracts use software code to automate tasks, thereby shaving hours off a range of business processes.Savings – Smart contracts save you money since they knock out the presence of an intermediary. You would, for instance, have to pay a notary to witness your transaction.
Accuracy – Automated contracts are not only faster and cheaper but also avoid the errors that come from manually filling out heaps of forms.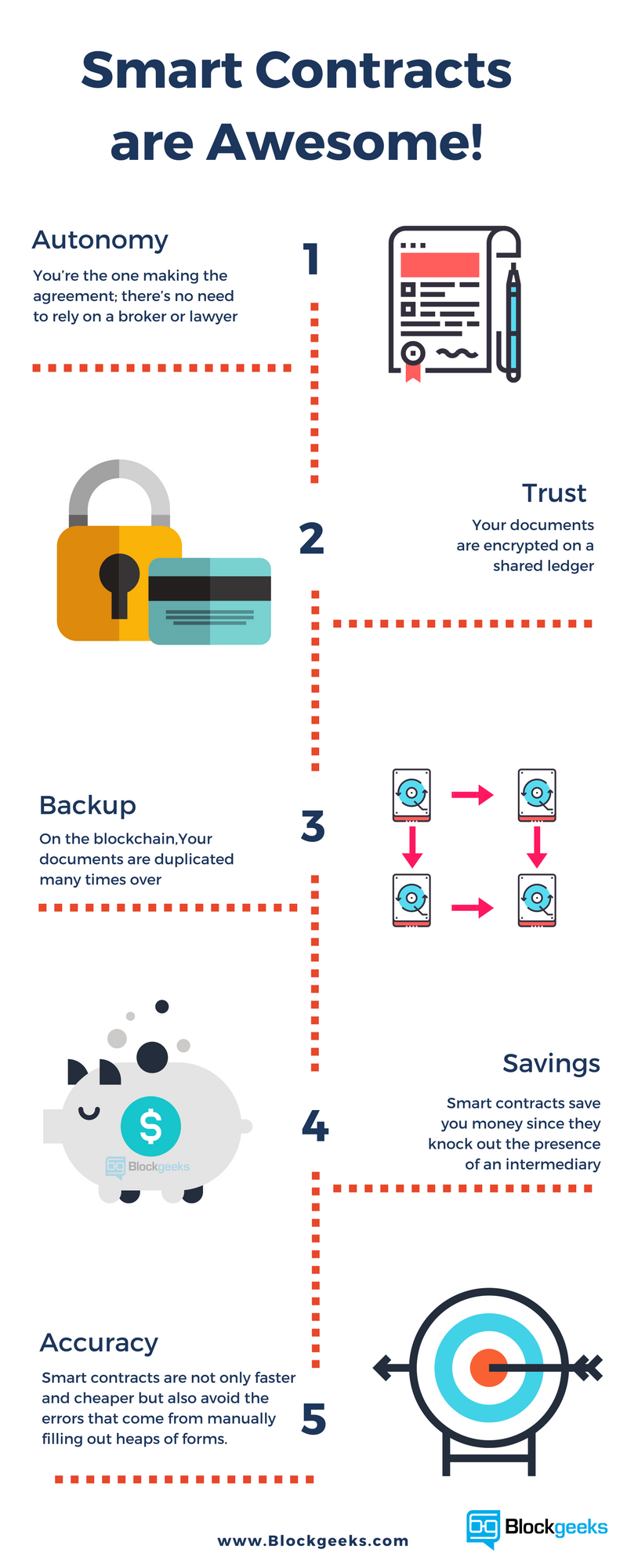
Here’s how Jeff Garzik, owner of blockchain services Bloq, described smart contracts:“Smart contracts … guarantee a very, very specific set of outcomes. There’s never any confusion and there’s never any need for litigation.”

“Smart Contracts are where the rubber meets the road for businesses and blockchain technology. While a few highly specialized distributed financial services use cases for blockchain have appeared—for example, payment ledger services for the Yangon Stock Exchange in Myanmar. Its services on top of blockchain that are really interesting.
In the Yangon Exchange, it solves the problem of distributed settlement in a trading system that only synchronizes trades twice a day.
But the autonomous execution capacities of smart contracts extends the transactional security assurance of blockchain into situations where complex, evolving context transitions are required. And it’s this possibility that has Amazon, Microsoft Azure and IBM Bluemix rolling out Blockchain-as-a-Service (Baas) from the cloud.” – Patrick Hubbard, Head Geek, SolarWinds
Now for Problems
Smart contracts are far from perfect. What if bugs get in the code? Or how should governments regulate such contracts? Or, how would governments tax these smart contract transactions? As a case in point, remember my rental situation?
What happens if I send the wrong code, or, as lawyer Bill Marino points out, I send the right code, but my apartment is condemned (i.e., taken for public use without my consent) before the rental date arrives? If this were the traditional contract, I could rescind it in court, but the blockchain is a different situation.
The contract performs, no matter what.The list of challenges goes on and on. Experts are trying to unravel them, but these critical issues do dissuade potential adopters from signing on. And here’s To the Future of Smart Contracts… Part of the future of smart contracts lies in entangling these issues.
In Cornell Tech, for instance, lawyers, who insist that smart contracts will enter our everyday life, have dedicated themselves to researching these concerns.
Actually, when it comes to smart contracts, we’re stepping into a sci-fi screen. The IT resource center, Search Compliance suggests that smart contracts may impact changes in certain industries, such as law.
In that case, lawyers will transfer from writing traditional contracts to producing standardized smart contract templates, similar to the standardized traditional contracts that you’ll find on LegalZoom.
Other industries such as...continue reading:
https://blockgeeks.com/guides/smart-contracts/-
Francisco Gimeno - BC Analyst I was talking yesterday to some friends who work as lawyers. They were telling me they have so much work they can't stop and read about smart contracts, block chain, etc.... well, beyond my personal opinion that if you are overwhelmed by work it means your planning is not so good, I told them that horses' owners at the end of the 19th century were also overwhelmed as there was a big transport business for them but because of that they didn't see the sign of the times and they lost everything to the motor vehicles. In an era of smartphones and smart everything, smart contracts are the solution to many issues nowadays and when on the mainstream this is going to affect every sector and every person. I know more than yesterday about this by reading this article, and that is enough for me.
-






