Bitcoin
Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency and worldwide payment system. It is the first decentralized digital currency, as the system works without a central bank or single administrator. The network is peer-to-peer.
- Birthday August 18th, 2008
- Country United States
-
Profession - Describe your professional skills or service here
Learn about Bitcoin
Buy Bitcoin
Trade in Bitcoin
Invest in Bitcon
Use Bitcoin to make payments
Send Bitcoin to friends and people you love or care about.
Discover the ecosystem of Blockchain
Follow us after you've created a free account here on BC. Bitcoin will follow you back!
Share Bitcoin content with friends and what you discover to your BC blockchain page, just like this one. Thanks for helping others around the world discover and learn about Bitcoin!
- 14 followers
- 543 following
- 21 posts
- 11 likes received
- 1 comment received
- 35 points
- About Bitcoin 2 items
- Blockchain Use Cases 1 items
- FAQ 1 items
- Introduction To Bitcoin 5 items
- Participate 2 items
- Stories We Like 19 items
-
About bitcoin.org
Bitcoin.org is dedicated to help Bitcoin to develop in a sustainable way.Who owns bitcoin.org?
Bitcoin.org was originally registered and owned by Bitcoin's first two developers, Satoshi Nakamoto and Martti Malmi.
When Nakamoto left the project, he gave ownership of the domain to
additional people, separate from the Bitcoin developers, to spread
responsibility and prevent any one person or group from easily gaining
control over the Bitcoin project.
From 2011 to 2013, the site was primarily used for releasing new
versions of the software now called Bitcoin Core. In 2013, the site was
redesigned into its current form, adding numerous pages, listing
additional Bitcoin software, and creating the translation system.
Developer documentation was added in 2014.
Today the site is an independent open source project with
contributors from around the world. Final publication authority is held
by the co-owners, but all regular activity is organized through the
public pull request process and managed by the site co-maintainers.
Bitcoin.org is not Bitcoin's official website. Just like nobody
owns the email technology, nobody owns the Bitcoin network. As such,
nobody can speak with authority in the name of Bitcoin.Then... who controls Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is controlled by all Bitcoin users around the world.
Developers are improving the software but they can't force a change in
the rules of the Bitcoin protocol because all users are free to choose
what software they use. In order to stay compatible with each other, all
users need to use software complying with the same rules.
Bitcoin can
only work decently with a complete consensus between all users.
Therefore, all users and developers have strong incentives to adopt and
protect this consensus.Mission
- Inform users to protect them from common mistakes.
- Give an accurate description of Bitcoin properties, potential uses and limitations.
- Display transparent alerts and events regarding the Bitcoin network.
- Invite talented humans to help with Bitcoin development at many levels.
- Provide visibility to the large scale Bitcoin ecosystem.
- Improve Bitcoin worldwide accessibility with internationalization.
- Remain a neutral informative resource about Bitcoin.
Help us
You can report any problem or help to improve bitcoin.org on GitHub
by opening an issue or a pull request in English. When submitting a
pull request, please take required time to discuss your changes and
adapt your work. You can help with translations by joining a team on Transifex.
Please don't ask for promotion for your personal business or website,
except for special cases like conferences. Many thanks to all
contributors who are spending time improving bitcoin.org!
- Admin and
- Ahmet Jamal
-
- 1
Bitcoin Bitcoin Bitcoin is hot in the news and has risen dramatically lately. You can learn more about Bitcoin right here on BC! As always, invest wisely, sensibly and invest only what you can afford.- 10 1 vote
- Reply
-
This video is also showing now on BCtv here, for larger screen viewing on your desktop, laptop and connected smart tv.
Subscribe to our Free Financial Newsletter:
http://crushthestreet.com
For more information on how to profit from this massive world-changing trend, visit CrushTheStreet.com/bitcoin.
- Paula Nita and
- Bitcoin
-
Bitcoin Bitcoin Share Blockchain videos like this one with friends. Blockchain is the protocol that enables Bitcoin an over 1000 Cryptocurrencies today. The blockchain is disrupting every industry one way or the other and skills in this area are highly sought after. Learn more to keep ahead
-
Over the past year, the price of a Bitcoin has skyrocketed from less than $800 to nearly $20,000 — a meteoric rise that financial insiders say is no different than the escalating cost of a tulip in seventeenth-century Amsterdam.
Is it a bubble? Who cares!This video is also showing now on BCtv here, for larger screen viewing on your desktop, laptop and connected smart tv.
As VICE News' Jay Kang told us, “It’s impossible right now to not get rich if you own any Bitcoin.”
Kang first got the Bitcoin bug in July, initially investing $4000, upping it to $9000, then fearing a crash, betting his entire crypto-cache on a random soccer game (which he lost).
A former aspiring professional poker player, Kang bounced back undeterred, and with the surging price of the currency, Bitcoin mania has taken over his life. He claims 10 percent of his net worth is now invested in cryptocurrency.
Subscribe to VICE News here: http://bit.ly/Subscribe-to-VICE-News
-
CNBC's Bob Pisani discusses what factors play into varying bitcoin prices.
» Subscribe to CNBC: http://cnb.cx/SubscribeCNBCThis video is also showing now on BCtv here, for larger screen viewing on your desktop, laptop and connected smart tv.
-
By
 Bitcoin
Bitcoin - 0 comments
- 0 likes
- Like
- Share
-
By
-
Oliver Bussmann is founder and managing partner at Bussmann Advisory, the president of not-for-profit Crypto Valley Association and former group CIO and managing director at UBS.
The following article is an exclusive contribution to CoinDesk's 2017 in Review.
2017 was a year of tremendous growth for blockchain, though not in the expected ways.At the beginning of this year, I and others predicted that 2017 would be the year that blockchain moved from proof-of-concepts into production.
We did see some notable successes in this regard.Ripple became a fully operational platform with over 100 members and payment volumes in the billions, and industries began to form blockchain business networks, for example, the Digital Trade Chain consortium (DTC) in trade finance.
But overall, I expected to see more "go lives" than we did. On the other hand, I don't think anyone expected the unprecedented growth in the market capitalization of cryptocurrencies or the related ICO boom.So, what will the new year bring? Despite the obvious perils in making predictions, I feel confident that, among other things, we will see the following:- Blockchain solutions will continue to come into production as the "low-hanging fruit" are addressed.
- Cryptocurrencies will continue to grow, fueled by traditional asset management players and techniques.
- Companies will focus on changing business models as blockchain begins to transform market structures.
- New ecosystems with smart contract technology will arise as integration platforms between existing industries.
- The ICO will become "professionalized" and morph into IPO 2.0.
- Scalability and performance of blockchains will become a critical issue, and there will be interesting new approaches
- People will increasingly recognize that local blockchain ecosystems are a critical success factor.
Low-hanging fruit
Although it was quieter than expected this year, I believe we will continue to see blockchain solutions come into production as enterprises address the "low-hanging fruit" by digitizing businesses and use cases where blockchain can make the most impact.In fintech, the two most promising use cases remain payments (where there are $50–60 billion of potential savings to be had) and trade finance (which stands to save some $15 billion).
As we saw payments do in 2017, I expect we will see trade finance begin to go live on blockchain in 2018. In payments, momentum will pick up and volumes will increase as larger banks, including correspondent banks, get into the act. These players will be tempted by the advantages blockchain brings in terms of real-time processing, lower risk profiles, lower costs and transparency.
Blockchain can serve as a stick as well as a carrot, simply by proving that there are better alternatives to the status quo in many industries. We can imagine, as an example, that blockchain has had a hand to play in the European Banking Authority's EU-wide transparency exercises.
We were all somewhat surprised – if pleasantly so – by how well cryptocurrencies did in 2017 as a speculative asset. Indeed, growth was spectacular, with the asset class rising from $14 billion in December 2016 to over $450 billion in December 2017 in terms of market capitalization.
I think this growth will continue to be fueled by traditional asset management approaches, including bitcoin futures, crypto hedge funds and the like, all of which will increase the demand for cryptocurrencies and tokens.New business models
As blockchain continues to change market structures, companies will increasingly focus on changing business models.In a world where middlemen are becoming obsolete, companies will have to learn to stop thinking in silos and be more open to becoming partners in ecosystems or on broader platforms.
That, in turn, means deciding what kinds of business models they want – whether it's platform plays, product plays, omni-channel strategies, and so on.
These discussions will become multi-dimensional, encompassing both existing services and, increasingly, the new kinds of services that blockchain enables – particularly as blockchain combines with IoT and AI to create new kinds of marketplaces where industry silos come down in favor of broad, horizontal structures.
One of the most satisfying parts of 2017 for me was being able to see this start to happen close-hand among some of the companies I have the privilege to work with. (See disclosures below.)Deon Digital has partnered with Mercedes Benz to develop a new operating system that will help break down silos in the mobility space.
Skycell is a good example of IoT and blockchain opening up the pharmaceutical supply chain to embrace payments, invoicing and insurance. TEND is rethinking investment management by creating a Sharing Economy 2.0 for high-value assets.
One space I think we should keep a particular eye on in 2018 is the fund industry, where firms like Melonport are using blockchain to rethink asset management. I think we will see more of this, and that the fund industry will start to be significantly disrupted next year.
This will start with the management of crypto assets, but over time we will see traditional assets increasingly being tokenized, migrated onto blockchains and managed on-chain.The morphing of ICOs
With startups raising over $3.5 billion in ICOs, 2017 was clearly the year of the token launch.To me, though, the ICO boom is significant, not necessarily because of the amounts raised, but because we are seeing the beginnings of the democratization of venture capital.
And though the concept had a great 2017, change will come to the world of ICOs in 2018 as more traditional players get involved.
Over the next 12-18 months, I expect people with experience and expertise in the IPO world will embrace tokenization as a technical platform, and the whole business will be professionalized, with book building, pricing, startup evaluation and so on happening more along traditional lines.
As we've already begun to see, it will be harder to get funding simply on the back of a white paper. Investors will demand sound business plans and high levels of transparency, with all that entails.Scalability and ecosystems
One of the key challenges of existing blockchain technology is scale and performance. I predict that next year we will see alternatives to current blockchain technologies that will be more scalable, faster and minimize energy consumption.
IOTA, which has gained a lot of traction lately, is, I think, a project to watch in this regard.
I also believe people will increasingly find that local blockchain ecosystems, where critical services are co-located in one geographical area, are critical success factors for blockchain projects. This is certainly what we see in the "Crypto Valley" in Switzerland.
As the President of the Crypto Valley Association, I hope readers will forgive me for predicting – or at the least, pitching for – the continued success of Switzerland as a blockchain ecosystem.
Crypto Valley has a high concentration of all the services blockchain projects will need to raise money and set up shop, including legal, advisory, tax, accounting, smart contract platforms, KYC/AML utilities and marketing expertise.
This coupled with Switzerland’s other advantages, from its state-of-the-art infrastructure to its highly skilled workforce, will, in my opinion, mean it should remain a great draw for blockchain companies – in the new year and hopefully for many years to come.
Disclosure: Oliver Bussman is a strategic advisor to IOTA, Deon Digital and Tend, mentioned in this article.
Disagree? CoinDesk's 2017 in Review is ongoing – and open for submissions. Email [email protected] to pitch your article ideas.
-
By
 Bitcoin
Bitcoin - 2 comments
- 1 like
- Like
- Share
-
Bitcoin Bitcoin Share Blockchain stories like this one with friends. Blockchain is the protocol that enables Bitcoin an over 1000 Cryptocurrencies today. The blockchain is disrupting every industry one way or the other and skills in this area are highly sought after. Learn more to keep ahead
-
Just 1,000 bitcoin holders own 40 per cent of the market, according to a new report. These major investors, known as “whales”, could cause the value of the cryptocurrency to plummet at any point, it has been claimed.
Bitcoin hit a new record high on 8 December, soaring above the $17,600 mark. At the start of the year, it was worth $970. However, the cryptocurrency is notoriously volatile. Its value fell to below $14,000 on 10 December, before rising to more than $16,000 on 11 December. What's more, financial experts have suggested that bitcoin could be even more unstable than people thought.
1,000 holders own about 40 per cent of bitcoin, a new Bloomberg report claims, adding that the future of the cryptocurrency lies largely in these so-called bitcoin whales’ hands.
At current prices, each of them may be considering selling around half of their holdings, Aaron Brown, the former managing director and head of financial markets research at AQR Capital Management, told Bloomberg.
The report adds that many of the whales have know each other for several years, and can coordinate their moves by sharing information – which isn't illegal in the case of bitcoin.
According to a recent report, 16,381,204 bitcoin were in circulation as of mid-2017, and almost four million have been lost and may never be recovered.
This article originally used the word “people” about the biggest holders of bitcoin. Some of those owners are in fact groups and organisations, and the article has been edited to reflect that.
Reference:
According to a recent report, 16,381,204 bitcoin were in circulation as of mid-2017, and almost four million have been lost and may never be recovered.
-
By
 Bitcoin
Bitcoin - 0 comments
- 0 likes
- Like
- Share
-
By
-
When your cab driver starts talking about Bitcoin, it’s time to sell | Financial... (business.financialpost.com)Whether it’s the shoeshine boy of decades past, or the taxi driver
of more recent times, an old investing adage suggests that when somebody
you wouldn’t expect is talking stocks or giving you portfolio advice,
it’s time to sell.
And these days, it’s hard to find someone who isn’t talking about Bitcoin.
From
high school students discussing how to purchase fractions of the
digital currency over lunch at McDonald’s to YouTube celebrities giving
advice on how to make a quick buck, or thousand, the mania around the
cryptocurrency has been mounting for weeks
On Sunday night, it grew even stronger, as Cboe Global Markets Inc. launched the trading
of Bitcoin futures contracts, leading to another price surge and the
imposition of trading halts to quell the frenzied activity.
On
Monday, the rise continued, as prices for the contract expiring on Jan.
17 — the vast majority of CBOE Bitcoin futures traded so far have been
of the one-month variety — leapt more than US$3,100 to US$18,600 by late
afternoon.The
price of Bitcoin itself, as report by Coindesk.com, also surged Monday,
climbing nearly 13 cent to surpass US$17,000 for the first time.
“We’re
obviously dealing with a global phenomenon that everyone can
potentially partake in — both the creation of Bitcoin, but also
investing in it,” said Douglas Porter, chief economist at BMO Capital
Markets. “There is a place for it, and certainly the blockchain
technology does have a very important future. Having said that, every
great mania or bubble starts off with a very compelling story.
”The
most popular of many unregulated digital currencies with blockchain as
the underpinning technology, Bitcoin began 2017 just below US$1,000, and
is up more than 275 per cent in the past three months alone.“It
has — to some extent — gotten a stamp of legitimacy from the fact that
the CBOE has welcomed it, and the fact that so many central bank
officials globally are now looking at it,” Porter said, noting
speculation that the U.S.
Federal Reserve may eventually issue its own
cryptocurrency, and ensure Americans use it.“We’re definitely
hearing modern-day versions of the shoeshine boy story, which is usually
a pretty good signal that we’re getting close to the top.
Although,
history has show that manias can go on a lot longer than many people
believe is possible,” he added....continue reading: http://business.financialpost.com/technology/blockchain/when-your-cab-driver-starts-talking-about-bi...
-
Bitcoin traders and watchers have been busy heralding the entrance of
cryptocurrencies futures. What they should really be focused on is the
exit.
The first 24 hours of the Cboe Global Markets Inc.'s bitcoin
futures contract went pretty well.
By Monday evening, 3,969 of the
Cboe's main January contracts had been bought and sold -- not big by
established futures market standards, but more than many people
expected. With some brokers barring shorting, there was some concerns
that buyers wouldn't be able to find sellers.
That didn't happen. There
also wasn't a huge flood of people waiting to bet against bitcoin and
driving the price of the contract down. Instead, it ended up $3,545 on
the day at $18,545. Bitcoin rose, too. As much as bitcoin bulls
might want to use the smooth start of trading to contend that the
cryptocurrency and its price are more solid than critics contend, the
real test won't come until Jan. 17.
That's when the Cboe's first main
contract expires. And as any futures trader knows, getting out can be
trickier than getting in.
Less Buzz
There
already are some troublesome signs. On Tuesday, the price of the
January contract was down $815, and volume was much lower in the second
day of trading.
But the biggest problem could be the persistent, and
unusually large, gap between the price of bitcoins and the futures
contract. That spread was more than $1,000, or 6 percent, as of Tuesday
morning, though it had been double that a day earlier....continue reading on Bloomberg: https://www.bloomberg.com/gadfly/articles/2017-12-12/bitcoin-bulls-should-focus-on-futures-exit-not-...
-
By
 Bitcoin
Bitcoin - 0 comments
- 0 likes
- Like
- Share
-
By
-
Hi it’s Invest Diva’s Kiana with News BTC and here is your
crypotocurrency update. After a big day for Bitcoin in the futures
market, Ethereum, the second largest cryptocurrency by market cap, still
struggles to break above the key resistance level of $484 versus the
USD.
Ethereum has been considered Bitcoin’s direct competitor by many
investors, but its price is nowhere as volatile as Bitcoin price.
Therefore, Ethereum is less likely to be driving up in a bubble, and
carries less crash risk as of today. On the corporate side, some of the
largest banks in the world have revealed a pilot designed to simplify
compliance using Ethereum. The project was born out of UBS' London-based
fintech laboratory.
Now they have help from Barclays, Credit Suisse,
KBC, SIX and Thomson Reuters. Also known as the Massive Autonomous
Distributed Reconciliation (Madrec) platform, this project was designed
to make it easier for banks to reconcile a large amount of data about
their counterparties. But it’s not all sunshine and rainbows for the
Ethereum market players.
According to Mashable, A fake version of
popular wallet for Ethereum, called MyEtherWallet, is currently being
sold in Apple's App Store. The app is created by a developer called Nam
Le, with no ties to the makers of the original MyEtherWallet, which
currently exists only as a browser app.
So if you’re into Ethereum
investing, keep your coins safe and do your research before moving your
assets from one wallet to another. Thanks for watching, invest
responsibly, and I’ll see you with more updates tomorrow.
-
By
 Bitcoin
Bitcoin - 0 comments
- 0 likes
- Like
- Share
-
By
-
With the launch of bitcoin futures on the Cboe, BitGO CEO Mike Belshe discusses the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
» Subscribe to CNBC:
http://cnb.cx/SubscribeCNBC
About CNBC:This video is also showing now on BCtv here, for larger screen viewing on your desktop, laptop and connected smart tv.
From 'Wall Street' to 'Main Street' to award winning
original documentaries and Reality TV series, CNBC has you covered.
Experience special sneak peeks of your favorite shows, exclusive video
and more.
-
Tyler Winklevoss and Cameron Winklevoss, co-founders at Gemini, discuss
the positives of bitcoin, the cryptocurrency's potential to disrupt
gold, and the potential for a further twentyfold increase in the price
of bitcoin. They speak on "Bloomberg Daybreak: Americas."This video is also showing now on BCtv here, for larger screen viewing on your desktop, laptop and connected smart tv.
-
By Rob Wile
10:40 AM EST
Earlier this year, Nobel-winning Yale economist Robert Shiller called Bitcoin “the best example” of a speculative bubble there is right now.That was when the price of a single Bitcoin was still below $5,000.
As of Tuesday morning, the price is at nearly $17,000.In an email to MONEY on Monday, Shiller, who famously spotted a possible housing bubble before it actually blew up, said that it was “not easy to see” where Bitcoin is going.
He is also the author of the best-selling book, Irrational Exuberance.Its prices, he said, aren’t really reflective of anything other than people’s interest, though, he noted, interest levels are spreading “like a contagion,” meaning it has “aspects of a bubble.”
“The Bitcoin price is like a thermometer measuring the intensity of the epidemic,” he said.One reason for the intensity has something to do with how people think about Bitcoin: For many, cryptocurrencies have always been, and continue to be, an ideology.
“Bitcoin…is also a political movement, appealing to people who wish to see themselves freed from government regulation,” he said.Shiller also called for increased regulation, if only because things remain so uncertain.“Bitcoin is one of hundreds of cryptocurrencies.
Beyond the currencies themselves, there are exchanges and securities and futures markets. It is a big phenomenon. It is not easy to see where it is going.”Bitcoin futures started trading for the first time yesterday, revealing how volatile things remain in the cryptocurrency world.
Futures on the world’s most popular cryptocurrency surged as much as 26% in their debut session on the exchange, triggering two temporary trading halts designed to calm the market, Bloomberg reported.
“It is rare that you see something more volatile than Bitcoin, but we found it: Bitcoin futures,” Zennon Kapron, managing director of Shanghai-based consulting firm Kapronasia, told the news service.One analyst for Bitcoin news and research group Coindesk said Tuesday’s price movements indicate Bitcoin could hit $20,000 shortly.
“The ascending 10-day [moving average] favors further upside in prices, and suggests that any pullbacks are likely to be short-lived,” Coindesk’s Omkar Godbole said.
-
By
 Bitcoin
Bitcoin - 0 comments
- 0 likes
- Like
- Share
-
By
-
General
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a consensus network that enables a new payment system and a
completely digital money. It is the first decentralized peer-to-peer
payment network that is powered by its users with no central authority
or middlemen. From a user perspective, Bitcoin is pretty much like cash
for the Internet. Bitcoin can also be seen as the most prominent triple entry bookkeeping system in existence.
Who created Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is the first implementation of a concept called
"cryptocurrency", which was first described in 1998 by Wei Dai on the
cypherpunks mailing list, suggesting the idea of a new form of money
that uses cryptography to control its creation and transactions, rather
than a central authority. The first Bitcoin specification and proof of
concept was published in 2009 in a cryptography mailing list by Satoshi
Nakamoto. Satoshi left the project in late 2010 without revealing much
about himself. The community has since grown exponentially with many developers working on Bitcoin.
Satoshi's anonymity often raised unjustified concerns, many of which
are linked to misunderstanding of the open-source nature of Bitcoin. The
Bitcoin protocol and software are published openly and any developer
around the world can review the code or make their own modified version
of the Bitcoin software. Just like current developers, Satoshi's
influence was limited to the changes he made being adopted by others and
therefore he did not control Bitcoin. As such, the identity of
Bitcoin's inventor is probably as relevant today as the identity of the
person who invented paper.
Who controls the Bitcoin network?
Nobody owns the Bitcoin network much like no one owns the technology
behind email. Bitcoin is controlled by all Bitcoin users around the
world. While developers are improving the software, they can't force a
change in the Bitcoin protocol because all users are free to choose what
software and version they use. In order to stay compatible with each
other, all users need to use software complying with the same rules.
Bitcoin can only work correctly with a complete consensus among all
users. Therefore, all users and developers have a strong incentive to
protect this consensus.
How does Bitcoin work?
From a user perspective, Bitcoin is nothing more than a mobile app or
computer program that provides a personal Bitcoin wallet and allows a
user to send and receive bitcoins with them. This is how Bitcoin works
for most users.
Behind the scenes, the Bitcoin network is sharing a public ledger
called the "block chain". This ledger contains every transaction ever
processed, allowing a user's computer to verify the validity of each
transaction. The authenticity of each transaction is protected by
digital signatures corresponding to the sending addresses, allowing all
users to have full control over sending bitcoins from their own Bitcoin
addresses. In addition, anyone can process transactions using the
computing power of specialized hardware and earn a reward in bitcoins
for this service. This is often called "mining". To learn more about
Bitcoin, you can consult the dedicated page and the original paper.
Is Bitcoin really used by people?
Yes. There are a growing number of businesses
and individuals using Bitcoin. This includes brick-and-mortar
businesses like restaurants, apartments, and law firms, as well as
popular online services such as Namecheap, Overstock.com, and Reddit.
While Bitcoin remains a relatively new phenomenon, it is growing fast.
At the end of April 2017, the total value of all existing bitcoins exceeded 20 billion US dollars, with millions of dollars worth of bitcoins exchanged daily.
How does one acquire bitcoins?
- As payment for goods or services.
- Purchase bitcoins at a Bitcoin exchange.
- Exchange bitcoins with someone near you.
- Earn bitcoins through competitive mining.
While it may be possible to find individuals who wish to sell
bitcoins in exchange for a credit card or PayPal payment, most exchanges
do not allow funding via these payment methods. This is due to cases
where someone buys bitcoins with PayPal, and then reverses their half of
the transaction. This is commonly referred to as a chargeback.
How difficult is it to make a Bitcoin payment?
Bitcoin payments are easier to make than debit or credit card
purchases, and can be received without a merchant account. Payments are
made from a wallet application, either on your computer or smartphone,
by entering the recipient's address, the payment amount, and pressing
send. To make it easier to enter a recipient's address, many wallets can
obtain the address by scanning a QR code or touching two phones
together with NFC technology.
What are the advantages of Bitcoin?
- Payment freedom - It is possible to send and
receive bitcoins anywhere in the world at any time. No bank holidays. No
borders. No bureaucracy. Bitcoin allows its users to be in full control
of their money.
- Choose your own fees - There is no fee to receive
bitcoins, and many wallets let you control how large a fee to pay when
spending. Higher fees can encourage faster confirmation
of your transactions. Fees are unrelated to the amount transferred, so
it's possible to send 100,000 bitcoins for the same fee it costs to send
1 bitcoin. Additionally, merchant processors exist to assist merchants
in processing transactions, converting bitcoins to fiat currency and
depositing funds directly into merchants' bank accounts daily. As these
services are based on Bitcoin, they can be offered for much lower fees
than with PayPal or credit card networks.
- Fewer risks for merchants - Bitcoin transactions
are secure, irreversible, and do not contain customers’ sensitive or
personal information. This protects merchants from losses caused by
fraud or fraudulent chargebacks, and there is no need for PCI
compliance. Merchants can easily expand to new markets where either
credit cards are not available or fraud rates are unacceptably high. The
net results are lower fees, larger markets, and fewer administrative
costs. - Security and control - Bitcoin users are in full
control of their transactions; it is impossible for merchants to force
unwanted or unnoticed charges as can happen with other payment methods.
Bitcoin payments can be made without personal information tied to the
transaction. This offers strong protection against identity theft.
Bitcoin users can also protect their money with backup and encryption. - Transparent and neutral - All information
concerning the Bitcoin money supply itself is readily available on the
block chain for anybody to verify and use in real-time. No individual or
organization can control or manipulate the Bitcoin protocol because it
is cryptographically secure. This allows the core of Bitcoin to be
trusted for being completely neutral, transparent and predictable.
What are the disadvantages of Bitcoin?
- Degree of acceptance - Many people are still
unaware of Bitcoin. Every day, more businesses accept bitcoins because
they want the advantages of doing so, but the list remains small and
still needs to grow in order to benefit from network effects. - Volatility - The total value
of bitcoins in circulation and the number of businesses using Bitcoin
are still very small compared to what they could be. Therefore,
relatively small events, trades, or business activities can
significantly affect the price. In theory, this volatility will decrease
as Bitcoin markets and the technology matures. Never before has the
world seen a start-up currency, so it is truly difficult (and exciting)
to imagine how it will play out. - Ongoing development - Bitcoin software is still in
beta with many incomplete features in active development. New tools,
features, and services are being developed to make Bitcoin more secure
and accessible to the masses. Some of these are still not ready for
everyone. Most Bitcoin businesses are new and still offer no insurance.
In general, Bitcoin is still in the process of maturing.
Why do people trust Bitcoin?
Much of the trust in Bitcoin comes from the fact that it requires no
trust at all. Bitcoin is fully open-source and decentralized. This means
that anyone has access to the entire source code at any time. Any
developer in the world can therefore verify exactly how Bitcoin works.
All transactions and bitcoins issued into existence can be transparently
consulted in real-time by anyone. All payments can be made without
reliance on a third party and the whole system is protected by heavily
peer-reviewed cryptographic algorithms like those used for online
banking. No organization or individual can control Bitcoin, and the
network remains secure even if not all of its users can be trusted.
Can I make money with Bitcoin?
You should never expect to get rich with Bitcoin or any emerging
technology. It is always important to be wary of anything that sounds
too good to be true or disobeys basic economic rules.
Bitcoin is a growing space of innovation and there are business
opportunities that also include risks. There is no guarantee that
Bitcoin will continue to grow even though it has developed at a very
fast rate so far. Investing time and resources on anything related to
Bitcoin requires entrepreneurship. There are various ways to make money
with Bitcoin such as mining, speculation or running new businesses. All
of these methods are competitive and there is no guarantee of profit. It
is up to each individual to make a proper evaluation of the costs and
the risks involved in any such project.
Is Bitcoin fully virtual and immaterial?
Bitcoin is as virtual as the credit cards and online banking networks
people use everyday. Bitcoin can be used to pay online and in physical
stores just like any other form of money. Bitcoins can also be exchanged
in physical form such as the Denarium coins,
but paying with a mobile phone usually remains more convenient. Bitcoin
balances are stored in a large distributed network, and they cannot be
fraudulently altered by anybody. In other words, Bitcoin users have
exclusive control over their funds and bitcoins cannot vanish just
because they are virtual.
Is Bitcoin anonymous?
Bitcoin is designed to allow its users to send and receive payments
with an acceptable level of privacy as well as any other form of money.
However, Bitcoin is not anonymous and cannot offer the same level of
privacy as cash. The use of Bitcoin leaves extensive public records. Various mechanisms
exist to protect users' privacy, and more are in development. However,
there is still work to be done before these features are used correctly
by most Bitcoin users.
Some concerns have been raised that private transactions could be
used for illegal purposes with Bitcoin. However, it is worth noting that
Bitcoin will undoubtedly be subjected to similar regulations that are
already in place inside existing financial systems. Bitcoin cannot be
more anonymous than cash and it is not likely to prevent criminal
investigations from being conducted. Additionally, Bitcoin is also
designed to prevent a large range of financial crimes.
What happens when bitcoins are lost?
When a user loses his wallet, it has the effect of removing money out
of circulation. Lost bitcoins still remain in the block chain just like
any other bitcoins. However, lost bitcoins remain dormant forever
because there is no way for anybody to find the private key(s) that
would allow them to be spent again. Because of the law of supply and
demand, when fewer bitcoins are available, the ones that are left will
be in higher demand and increase in value to compensate.
Can Bitcoin scale to become a major payment network?
The Bitcoin network can already process a much higher number of
transactions per second than it does today. It is, however, not entirely
ready to scale to the level of major credit card networks. Work is
underway to lift current limitations, and future requirements are well
known. Since inception, every aspect of the Bitcoin network has been in a
continuous process of maturation, optimization, and specialization, and
it should be expected to remain that way for some years to come. As
traffic grows, more Bitcoin users may use lightweight clients, and full
network nodes may become a more specialized service. For more details,
see the Scalability page on the Wiki.
Legal
Is Bitcoin legal?
To the best of our knowledge, Bitcoin has not been made illegal
by legislation in most jurisdictions. However, some jurisdictions (such
as Argentina and Russia) severely restrict or ban foreign currencies.
Other jurisdictions (such as Thailand) may limit the licensing of
certain entities such as Bitcoin exchanges.
Regulators from various jurisdictions are taking steps to provide
individuals and businesses with rules on how to integrate this new
technology with the formal, regulated financial system. For example, the
Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), a bureau in the United
States Treasury Department, issued non-binding guidance on how it
characterizes certain activities involving virtual currencies.
Is Bitcoin useful for illegal activities?
Bitcoin is money, and money has always been used both for legal and
illegal purposes. Cash, credit cards and current banking systems widely
surpass Bitcoin in terms of their use to finance crime. Bitcoin can
bring significant innovation in payment systems and the benefits of such
innovation are often considered to be far beyond their potential
drawbacks.
Bitcoin is designed to be a huge step forward in making money more
secure and could also act as a significant protection against many forms
of financial crime. For instance, bitcoins are completely impossible to
counterfeit. Users are in full control of their payments and cannot
receive unapproved charges such as with credit card fraud. Bitcoin
transactions are irreversible and immune to fraudulent chargebacks.
Bitcoin allows money to be secured against theft and loss using very
strong and useful mechanisms such as backups, encryption, and multiple
signatures.
Some concerns have been raised that Bitcoin could be more attractive
to criminals because it can be used to make private and irreversible
payments. However, these features already exist with cash and wire
transfer, which are widely used and well-established. The use of Bitcoin
will undoubtedly be subjected to similar regulations that are already
in place inside existing financial systems, and Bitcoin is not likely to
prevent criminal investigations from being conducted. In general, it is
common for important breakthroughs to be perceived as being
controversial before their benefits are well understood. The Internet is
a good example among many others to illustrate this.
Can Bitcoin be regulated?
The Bitcoin protocol itself cannot be modified without the
cooperation of nearly all its users, who choose what software they use.
Attempting to assign special rights to a local authority in the rules of
the global Bitcoin network is not a practical possibility. Any rich
organization could choose to invest in mining hardware to control half
of the computing power of the network and become able to block or
reverse recent transactions. However, there is no guarantee that they
could retain this power since this requires to invest as much than all
other miners in the world.
It is however possible to regulate the use of Bitcoin in a similar
way to any other instrument. Just like the dollar, Bitcoin can be used
for a wide variety of purposes, some of which can be considered
legitimate or not as per each jurisdiction's laws. In this regard,
Bitcoin is no different than any other tool or resource and can be
subjected to different regulations in each country. Bitcoin use could
also be made difficult by restrictive regulations, in which case it is
hard to determine what percentage of users would keep using the
technology. A government that chooses to ban Bitcoin would prevent
domestic businesses and markets from developing, shifting innovation to
other countries. The challenge for regulators, as always, is to develop
efficient solutions while not impairing the growth of new emerging
markets and businesses.
What about Bitcoin and taxes?
Bitcoin is not a fiat currency with legal tender status in any
jurisdiction, but often tax liability accrues regardless of the medium
used. There is a wide variety of legislation in many different
jurisdictions which could cause income, sales, payroll, capital gains,
or some other form of tax liability to arise with Bitcoin.
What about Bitcoin and consumer protection?
Bitcoin is freeing people to transact on their own terms. Each user
can send and receive payments in a similar way to cash but they can also
take part in more complex contracts. Multiple signatures allow a
transaction to be accepted by the network only if a certain number of a
defined group of persons agree to sign the transaction. This allows
innovative dispute mediation services to be developed in the future.
Such services could allow a third party to approve or reject a
transaction in case of disagreement between the other parties without
having control on their money. As opposed to cash and other payment
methods, Bitcoin always leaves a public proof that a transaction did
take place, which can potentially be used in a recourse against
businesses with fraudulent practices.
It is also worth noting that while merchants usually depend on their
public reputation to remain in business and pay their employees, they
don't have access to the same level of information when dealing with new
consumers. The way Bitcoin works allows both individuals and businesses
to be protected against fraudulent chargebacks while giving the choice
to the consumer to ask for more protection when they are not willing to
trust a particular merchant.
Economy
How are bitcoins created?
New bitcoins are generated by a competitive and decentralized process
called "mining". This process involves that individuals are rewarded by
the network for their services. Bitcoin miners are processing
transactions and securing the network using specialized hardware and are
collecting new bitcoins in exchange.
The Bitcoin protocol is designed in such a way that new bitcoins are
created at a fixed rate. This makes Bitcoin mining a very competitive
business. When more miners join the network, it becomes increasingly
difficult to make a profit and miners must seek efficiency to cut their
operating costs. No central authority or developer has any power to
control or manipulate the system to increase their profits. Every
Bitcoin node in the world will reject anything that does not comply with
the rules it expects the system to follow.
Bitcoins are created at a decreasing and predictable rate. The number
of new bitcoins created each year is automatically halved over time
until bitcoin issuance halts completely with a total of 21 million
bitcoins in existence. At this point, Bitcoin miners will probably be
supported exclusively by numerous small transaction fees.
Why do bitcoins have value?
Bitcoins have value because they are useful as a form of money.
Bitcoin has the characteristics of money (durability, portability,
fungibility, scarcity, divisibility, and recognizability) based on the
properties of mathematics rather than relying on physical properties
(like gold and silver) or trust in central authorities (like fiat
currencies). In short, Bitcoin is backed by mathematics. With these
attributes, all that is required for a form of money to hold value is
trust and adoption. In the case of Bitcoin, this can be measured by its
growing base of users, merchants, and startups. As with all currency,
bitcoin's value comes only and directly from people willing to accept
them as payment.
What determines bitcoin’s price?
The price of a bitcoin is determined by supply and demand. When
demand for bitcoins increases, the price increases, and when demand
falls, the price falls. There is only a limited number of bitcoins in
circulation and new bitcoins are created at a predictable and decreasing
rate, which means that demand must follow this level of inflation to
keep the price stable. Because Bitcoin is still a relatively small
market compared to what it could be, it doesn't take significant amounts
of money to move the market price up or down, and thus the price of a
bitcoin is still very volatile.
Bitcoin price over time: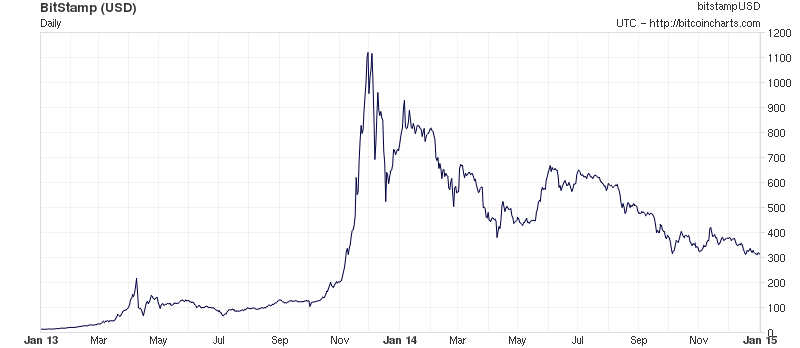
Can bitcoins become worthless?
Yes. History is littered with currencies that failed and are no longer used, such as the German Mark during the Weimar Republic and, more recently, the Zimbabwean dollar.
Although previous currency failures were typically due to
hyperinflation of a kind that Bitcoin makes impossible, there is always
potential for technical failures, competing currencies, political issues
and so on. As a basic rule of thumb, no currency should be considered
absolutely safe from failures or hard times. Bitcoin has proven reliable
for years since its inception and there is a lot of potential for
Bitcoin to continue to grow. However, no one is in a position to predict
what the future will be for Bitcoin.
Is Bitcoin a bubble?
A fast rise in price does not constitute a bubble. An artificial
over-valuation that will lead to a sudden downward correction
constitutes a bubble. Choices based on individual human action by
hundreds of thousands of market participants is the cause for bitcoin's
price to fluctuate as the market seeks price discovery. Reasons for
changes in sentiment may include a loss of confidence in Bitcoin, a
large difference between value and price not based on the fundamentals
of the Bitcoin economy, increased press coverage stimulating speculative
demand, fear of uncertainty, and old-fashioned irrational exuberance
and greed.
Is Bitcoin a Ponzi scheme?
A Ponzi scheme is a fraudulent investment operation that pays returns
to its investors from their own money, or the money paid by subsequent
investors, instead of from profit earned by the individuals running the
business. Ponzi schemes are designed to collapse at the expense of the
last investors when there is not enough new participants.
Bitcoin is a free software project with no central authority.
Consequently, no one is in a position to make fraudulent representations
about investment returns. Like other major currencies such as gold,
United States dollar, euro, yen, etc. there is no guaranteed purchasing
power and the exchange rate floats freely. This leads to volatility
where owners of bitcoins can unpredictably make or lose money. Beyond
speculation, Bitcoin is also a payment system with useful and
competitive attributes that are being used by thousands of users and
businesses.
Doesn't Bitcoin unfairly benefit early adopters?
Some early adopters have large numbers of bitcoins because they took
risks and invested time and resources in an unproven technology that was
hardly used by anyone and that was much harder to secure properly. Many
early adopters spent large numbers of bitcoins quite a few times before
they became valuable or bought only small amounts and didn't make huge
gains. There is no guarantee that the price of a bitcoin will increase
or drop. This is very similar to investing in an early startup that can
either gain value through its usefulness and popularity, or just never
break through. Bitcoin is still in its infancy, and it has been designed
with a very long-term view; it is hard to imagine how it could be less
biased towards early adopters, and today's users may or may not be the
early adopters of tomorrow.
Won't the finite amount of bitcoins be a limitation?
Bitcoin is unique in that only 21 million bitcoins will ever be
created. However, this will never be a limitation because transactions
can be denominated in smaller sub-units of a bitcoin, such as bits -
there are 1,000,000 bits in 1 bitcoin. Bitcoins can be divided up to 8
decimal places (0.000 000 01) and potentially even smaller units if that
is ever required in the future as the average transaction size
decreases.
Won't Bitcoin fall in a deflationary spiral?
The deflationary spiral theory says that if prices are expected to
fall, people will move purchases into the future in order to benefit
from the lower prices. That fall in demand will in turn cause merchants
to lower their prices to try and stimulate demand, making the problem
worse and leading to an economic depression.
Although this theory is a popular way to justify inflation amongst
central bankers, it does not appear to always hold true and is
considered controversial amongst economists. Consumer electronics is one
example of a market where prices constantly fall but which is not in
depression. Similarly, the value of bitcoins has risen over time and yet
the size of the Bitcoin economy has also grown dramatically along with
it. Because both the value of the currency and the size of its economy
started at zero in 2009, Bitcoin is a counterexample to the theory
showing that it must sometimes be wrong.
Notwithstanding this, Bitcoin is not designed to be a deflationary
currency. It is more accurate to say Bitcoin is intended to inflate in
its early years, and become stable in its later years. The only time the
quantity of bitcoins in circulation will drop is if people carelessly
lose their wallets by failing to make backups. With a stable monetary
base and a stable economy, the value of the currency should remain the
same.
Isn't speculation and volatility a problem for Bitcoin?
This is a chicken and egg situation. For bitcoin's price to
stabilize, a large scale economy needs to develop with more businesses
and users. For a large scale economy to develop, businesses and users
will seek for price stability.
Fortunately, volatility does not affect the main benefits of Bitcoin
as a payment system to transfer money from point A to point B. It is
possible for businesses to convert bitcoin payments to their local
currency instantly, allowing them to profit from the advantages of
Bitcoin without being subjected to price fluctuations. Since Bitcoin
offers many useful and unique features and properties, many users choose
to use Bitcoin. With such solutions and incentives, it is possible that
Bitcoin will mature and develop to a degree where price volatility will
become limited.
What if someone bought up all the existing bitcoins?
Only a fraction of bitcoins issued to date are found on the exchange
markets for sale. Bitcoin markets are competitive, meaning the price of a
bitcoin will rise or fall depending on supply and demand. Additionally,
new bitcoins will continue to be issued for decades to come. Therefore
even the most determined buyer could not buy all the bitcoins in
existence. This situation isn't to suggest, however, that the markets
aren't vulnerable to price manipulation; it still doesn't take
significant amounts of money to move the market price up or down, and
thus Bitcoin remains a volatile asset thus far.
What if someone creates a better digital currency?
That can happen. For now, Bitcoin remains by far the most popular
decentralized virtual currency, but there can be no guarantee that it
will retain that position. There is already a set of alternative
currencies inspired by Bitcoin. It is however probably correct to assume
that significant improvements would be required for a new currency to
overtake Bitcoin in terms of established market, even though this
remains unpredictable. Bitcoin could also conceivably adopt improvements
of a competing currency so long as it doesn't change fundamental parts
of the protocol.
Transactions
Why do I have to wait for confirmation?
Receiving notification of a payment is almost instant with Bitcoin.
However, there is a delay before the network begins to confirm your
transaction by including it in a block. A confirmation means that there
is a consensus on the network that the bitcoins you received haven't
been sent to anyone else and are considered your property. Once your
transaction has been included in one block, it will continue to be
buried under every block after it, which will exponentially consolidate
this consensus and decrease the risk of a reversed transaction. Each
confirmation takes between a few seconds and 90 minutes, with 10 minutes
being the average. If the transaction pays too low a fee or is
otherwise atypical, getting the first confirmation can take much longer.
Every user is free to determine at what point they consider a
transaction sufficiently confirmed, but 6 confirmations is often considered to be as safe as waiting 6 months on a credit card transaction.
How much will the transaction fee be?
Transactions can be processed without fees, but trying to send free
transactions can require waiting days or weeks. Although fees may
increase over time, normal fees currently only cost a tiny amount. By
default, all Bitcoin wallets
listed on Bitcoin.org add what they think is an appropriate fee to your
transactions; most of those wallets will also give you chance to review
the fee before sending the transaction.
Transaction fees are used as a protection against users sending
transactions to overload the network and as a way to pay miners for
their work helping to secure the network. The precise manner in which
fees work is still being developed and will change over time. Because
the fee is not related to the amount of bitcoins being sent, it may seem
extremely low or unfairly high. Instead, the fee is relative to the
number of bytes in the transaction, so using multisig or spending
multiple previously-received amounts may cost more than simpler
transactions. If your activity follows the pattern of conventional
transactions, you won't have to pay unusually high fees.
What if I receive a bitcoin when my computer is powered off?
This works fine. The bitcoins will appear next time you start your
wallet application. Bitcoins are not actually received by the software
on your computer, they are appended to a public ledger that is shared
between all the devices on the network. If you are sent bitcoins when
your wallet client program is not running and you later launch it, it
will download blocks and catch up with any transactions it did not
already know about, and the bitcoins will eventually appear as if they
were just received in real time. Your wallet is only needed when you
wish to spend bitcoins.
What does "synchronizing" mean and why does it take so long?
Long synchronization time is only required with full node clients
like Bitcoin Core. Technically speaking, synchronizing is the process of
downloading and verifying all previous Bitcoin transactions on the
network. For some Bitcoin clients to calculate the spendable balance of
your Bitcoin wallet and make new transactions, it needs to be aware of
all previous transactions. This step can be resource intensive and
requires sufficient bandwidth and storage to accommodate the full size
of the block chain. For Bitcoin to remain secure, enough people should
keep using full node clients because they perform the task of validating
and relaying transactions.
Mining
What is Bitcoin mining?
Mining is the process of spending computing power to process
transactions, secure the network, and keep everyone in the system
synchronized together. It can be perceived like the Bitcoin data center
except that it has been designed to be fully decentralized with miners
operating in all countries and no individual having control over the
network. This process is referred to as "mining" as an analogy to gold
mining because it is also a temporary mechanism used to issue new
bitcoins. Unlike gold mining, however, Bitcoin mining provides a reward
in exchange for useful services required to operate a secure payment
network. Mining will still be required after the last bitcoin is issued.
How does Bitcoin mining work?
Anybody can become a Bitcoin miner by running software with
specialized hardware. Mining software listens for transactions broadcast
through the peer-to-peer network and performs appropriate tasks to
process and confirm these transactions. Bitcoin miners perform this work
because they can earn transaction fees paid by users for faster
transaction processing, and newly created bitcoins issued into existence
according to a fixed formula.
For new transactions to be confirmed, they need to be included in a
block along with a mathematical proof of work. Such proofs are very hard
to generate because there is no way to create them other than by trying
billions of calculations per second. This requires miners to perform
these calculations before their blocks are accepted by the network and
before they are rewarded. As more people start to mine, the difficulty
of finding valid blocks is automatically increased by the network to
ensure that the average time to find a block remains equal to 10
minutes. As a result, mining is a very competitive business where no
individual miner can control what is included in the block chain.
The proof of work is also designed to depend on the previous block to
force a chronological order in the block chain. This makes it
exponentially difficult to reverse previous transactions because this
requires the recalculation of the proofs of work of all the subsequent
blocks. When two blocks are found at the same time, miners work on the
first block they receive and switch to the longest chain of blocks as
soon as the next block is found. This allows mining to secure and
maintain a global consensus based on processing power.
Bitcoin miners are neither able to cheat by increasing their own
reward nor process fraudulent transactions that could corrupt the
Bitcoin network because all Bitcoin nodes would reject any block that
contains invalid data as per the rules of the Bitcoin protocol.
Consequently, the network remains secure even if not all Bitcoin miners
can be trusted.
Isn't Bitcoin mining a waste of energy?
Spending energy to secure and operate a payment system is hardly a
waste. Like any other payment service, the use of Bitcoin entails
processing costs. Services necessary for the operation of currently
widespread monetary systems, such as banks, credit cards, and armored
vehicles, also use a lot of energy. Although unlike Bitcoin, their total
energy consumption is not transparent and cannot be as easily measured.
Bitcoin mining has been designed to become more optimized over time
with specialized hardware consuming less energy, and the operating costs
of mining should continue to be proportional to demand. When Bitcoin
mining becomes too competitive and less profitable, some miners choose
to stop their activities. Furthermore, all energy expended mining is
eventually transformed into heat, and the most profitable miners will be
those who have put this heat to good use. An optimally efficient mining
network is one that isn't actually consuming any extra energy. While
this is an ideal, the economics of mining are such that miners
individually strive toward it.
How does mining help secure Bitcoin?
Mining creates the equivalent of a competitive lottery that makes it
very difficult for anyone to consecutively add new blocks of
transactions into the block chain. This protects the neutrality of the
network by preventing any individual from gaining the power to block
certain transactions. This also prevents any individual from replacing
parts of the block chain to roll back their own spends, which could be
used to defraud other users. Mining makes it exponentially more
difficult to reverse a past transaction by requiring the rewriting of
all blocks following this transaction.
What do I need to start mining?
In the early days of Bitcoin, anyone could find a new block using
their computer's CPU. As more and more people started mining, the
difficulty of finding new blocks increased greatly to the point where
the only cost-effective method of mining today is using specialized
hardware. You can visit BitcoinMining.com for more information.
Security
Is Bitcoin secure?
The Bitcoin technology - the protocol and the cryptography - has a
strong security track record, and the Bitcoin network is probably the
biggest distributed computing project in the world. Bitcoin's most
common vulnerability is in user error. Bitcoin wallet files that store
the necessary private keys can be accidentally deleted, lost or stolen.
This is pretty similar to physical cash stored in a digital form.
Fortunately, users can employ sound security practices to protect their money or use service providers that offer good levels of security and insurance against theft or loss.
Hasn't Bitcoin been hacked in the past?
The rules of the protocol and the cryptography used for Bitcoin are
still working years after its inception, which is a good indication that
the concept is well designed. However, security flaws
have been found and fixed over time in various software
implementations. Like any other form of software, the security of
Bitcoin software depends on the speed with which problems are found and
fixed. The more such issues are discovered, the more Bitcoin is gaining
maturity.
There are often misconceptions about thefts and security breaches
that happened on diverse exchanges and businesses. Although these events
are unfortunate, none of them involve Bitcoin itself being hacked, nor
imply inherent flaws in Bitcoin; just like a bank robbery doesn't mean
that the dollar is compromised. However, it is accurate to say that a
complete set of good practices and intuitive security solutions is
needed to give users better protection of their money, and to reduce the
general risk of theft and loss. Over the course of the last few years,
such security features have quickly developed, such as wallet
encryption, offline wallets, hardware wallets, and multi-signature
transactions.
Could users collude against Bitcoin?
It is not possible to change the Bitcoin protocol that easily. Any
Bitcoin client that doesn't comply with the same rules cannot enforce
their own rules on other users. As per the current specification, double
spending is not possible on the same block chain, and neither is
spending bitcoins without a valid signature. Therefore, It is not
possible to generate uncontrolled amounts of bitcoins out of thin air,
spend other users' funds, corrupt the network, or anything similar.
However, powerful miners could arbitrarily choose to block or reverse
recent transactions. A majority of users can also put pressure for some
changes to be adopted. Because Bitcoin only works correctly with a
complete consensus between all users, changing the protocol can be very
difficult and requires an overwhelming majority of users to adopt the
changes in such a way that remaining users have nearly no choice but to
follow. As a general rule, it is hard to imagine why any Bitcoin user
would choose to adopt any change that could compromise their own money.
Is Bitcoin vulnerable to quantum computing?
Yes, most systems relying on cryptography in general are, including
traditional banking systems. However, quantum computers don't yet exist
and probably won't for a while. In the event that quantum computing
could be an imminent threat to Bitcoin, the protocol could be upgraded
to use post-quantum algorithms. Given the importance that this update
would have, it can be safely expected that it would be highly reviewed
by developers and adopted by all Bitcoin users.
Help
I'd like to learn more. Where can I get help?
You can find more information and help on the resources and community pages or on the Wiki FAQ.
-
By
 Bitcoin
Bitcoin - 2 comments
- 0 likes
- Like
- Share
-
How to buy Bitcoin
There are several ways you can buy Bitcoin.
Use a Bitcoin Exchange
Our Bitcoin Exchange page, lists many different businesses that can help you buy Bitcoin using your bank account.
Discover people selling Bitcoin in your community
Local Bitcoins lets you
search and browse through various sellers of Bitcoin in your area.
Sellers have reviews and feedback scores to help you choose.
Use a Bitcoin ATM
Bitcoin ATMs work like a regular ATM, except they allow you to
deposit and withdrawal money so that you can buy and sell Bitcoin. Coin ATM Radar has an interactive map to help you find the closest Bitcoin ATM near you.
-
By
 Bitcoin
Bitcoin - 2 comments
- 0 likes
- Like
- Share
-
By
-
Support Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a protocol that was born from a small
community and has grown fast since. There are a lot of things you can do
to help Bitcoin to spread and improve over time.
Using Bitcoin
Using Bitcoin is
the first thing you can do to support Bitcoin. There are probably many
cases where it can make your life easier. You can accept payments and
make purchases with Bitcoin.
Be the network
If you have a good Internet connection, you can strengthen the Bitcoin network by keeping full node software running on your computer or server with port 8333 open. Full nodes are securing and relaying all transactions.
Mining
You can start mining bitcoins
to help processing transactions. In order to protect the network, you
should join smaller mining pools and prefer decentralized pools like P2Pool or pools with getblocktemplate (GBT) support.
Translate
You can help to increase Bitcoin availability by translating or
improving translations inside important parts of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Just pick a project you would like to help.
Bitcoin Core - Bitcoin.org - Bitcoin Wiki - Bitcoin Wallet (Android) - Electrum
Development
Bitcoin is free software. So if you are a developer, you can use your super-powers to do good and improve Bitcoin. Or you can build amazing new services or software that can use Bitcoin.
Donation
The easiest way to help is to donate
a few bitcoins to BitGive. Or you can help directly fund any project
related to Bitcoin that you believe will be helpful in the future.
Organizations
Many non-profit organizations
are dedicated to protecting and promoting Bitcoin. You can help these
groups by joining them and taking part in their projects, discussions
and events.
Spread
Speak about Bitcoin to interested people. Write about it on your
blog. Tell your favorite shops you would like to pay with Bitcoin. Help
to keep merchant directories up to date. Or be creative and make yourself a nice Bitcoin T-shirt.
Documentation
Bitcoin.org and the Bitcoin wiki
provide useful documentation and we are constantly improving the
information they contain. You can help to improve these resources and
keep them up to date.
Meet the communities
You can join Bitcoin communities
and talk with other Bitcoin enthusiasts. You can learn more about
Bitcoin every day, give help to new users and get involved in
interesting projects.
-
By
 Bitcoin
Bitcoin - 2 comments
- 0 likes
- Like
- Share
-
By
-
Some things you need to know
If you are about to explore Bitcoin, there are a
few things you should know. Bitcoin lets you exchange money in a
different way than with usual banks. As such, you should take time to
inform yourself before using Bitcoin for any serious transaction.
Bitcoin should be treated with the same care as your regular wallet, or
even more in some cases!
Securing your wallet
Like in real life, your wallet must be secured. Bitcoin makes it
possible to transfer value anywhere in a very easy way and it allows you
to be in control of your money. Such great features also come with
great security concerns. At the same time, Bitcoin can provide very high
levels of security if used correctly. Always remember that it is your
responsibility to adopt good practices in order to protect your money. Read more about securing your wallet.
Bitcoin price is volatile
The price of a bitcoin can unpredictably increase or decrease over a
short period of time due to its young economy, novel nature, and
sometimes illiquid markets. Consequently, keeping your savings with
Bitcoin is not recommended at this point. Bitcoin should be seen like a
high risk asset, and you should never store money that you cannot afford
to lose with Bitcoin. If you receive payments with Bitcoin, many
service providers can convert them to your local currency.
Bitcoin payments are irreversible
Any transaction issued with Bitcoin cannot be reversed, they can only
be refunded by the person receiving the funds. That means you should
take care to do business with people and organizations you know and
trust, or who have an established reputation. For their part, businesses
need to keep control of the payment requests they are displaying to
their customers. Bitcoin can detect typos and usually won't let you send
money to an invalid address by mistake. Additional services might exist
in the future to provide more choice and protection for the consumer.
Bitcoin is not anonymous
Some effort is required to protect your privacy with Bitcoin. All
Bitcoin transactions are stored publicly and permanently on the network,
which means anyone can see the balance and transactions of any Bitcoin
address. However, the identity of the user behind an address remains
unknown until information is revealed during a purchase or in other
circumstances. This is one reason why Bitcoin addresses should only be
used once. Always remember that it is your responsibility to adopt good
practices in order to protect your privacy. Read more about protecting your privacy.
Unconfirmed transactions aren't secure
Transactions don't start out as irreversible. Instead, they get a confirmation
score that indicates how hard it is to reverse them (see table). Each
confirmation takes between a few seconds and 90 minutes, with 10 minutes
being the average. If the transaction pays too low a fee or is
otherwise atypical, getting the first confirmation can take much longer.
Confirmations
Lightweight wallets
Bitcoin Core
0
Only safe if you trust the person paying you
1
Somewhat reliable
Mostly reliable
3
Mostly reliable
Highly reliable
6
Minimum recommendation for high-value bitcoin transfers
30
Recommendation during emergencies to allow human intervention
Bitcoin is still experimental
Bitcoin is an experimental new currency that is in active
development. Each improvement makes Bitcoin more appealing but also
reveals new challenges as Bitcoin adoption grows. During these growing
pains you might encounter increased fees, slower confirmations, or even
more severe issues. Be prepared for problems and consult a technical
expert before making any major investments, but keep in mind that nobody
can predict Bitcoin's future.
Government taxes and regulations
Bitcoin is not an official currency. That said, most jurisdictions
still require you to pay income, sales, payroll, and capital gains taxes
on anything that has value, including bitcoins. It is your
responsibility to ensure that you adhere to tax and other legal or regulatory mandates issued by your government and/or local municipalities.
-
By
 Bitcoin
Bitcoin - 2 comments
- 2 likes
- Like
- Share
-
By
-
How does Bitcoin work?
This is a question that often causes confusion. Here's a quick explanation!
The basics for a new user
As a new user, you can get started
with Bitcoin without understanding the technical details. Once you have
installed a Bitcoin wallet on your computer or mobile phone, it will
generate your first Bitcoin address and you can create more whenever you
need one. You can disclose your addresses to your friends so that they
can pay you or vice versa. In fact, this is pretty similar to how email
works, except that Bitcoin addresses should only be used once.
Balances - block chain
The block chain is a shared public ledger on which the entire
Bitcoin network relies. All confirmed transactions are included in the
block chain. This way, Bitcoin wallets can calculate their spendable
balance and new transactions can be verified to be spending bitcoins
that are actually owned by the spender. The integrity and the
chronological order of the block chain are enforced with cryptography.
Transactions - private keys
A transaction is a transfer of value between Bitcoin wallets that gets included in the block chain. Bitcoin wallets keep a secret piece of data called a private key
or seed, which is used to sign transactions, providing a mathematical
proof that they have come from the owner of the wallet. The signature
also prevents the transaction from being altered by anybody once it has
been issued. All transactions are broadcast between users and usually
begin to be confirmed by the network in the following 10 minutes,
through a process called mining.
Processing - mining
Mining is a distributed consensus system that is used to confirm
waiting transactions by including them in the block chain. It enforces a
chronological order in the block chain, protects the neutrality of the
network, and allows different computers to agree on the state of the
system. To be confirmed, transactions must be packed in a block
that fits very strict cryptographic rules that will be verified by the
network. These rules prevent previous blocks from being modified because
doing so would invalidate all following blocks. Mining also creates the
equivalent of a competitive lottery that prevents any individual from
easily adding new blocks consecutively in the block chain. This way, no
individuals can control what is included in the block chain or replace
parts of the block chain to roll back their own spends.
Going down the rabbit hole
This is only a very short and concise summary of the system. If you want to get into the details, you can read the original paper that describes the system's design, read the developer documentation, and explore the Bitcoin wiki.
-
Getting started with Bitcoin
Using Bitcoin to pay and get paid is easy and accessible to everyone.
How to use Bitcoin
1. Inform yourself
Bitcoin is different than what you know and use every day. Before
you start using Bitcoin, there are a few things that you need to know
in order to use it securely and avoid common pitfalls.
Read more
2. Choose your wallet
You can bring a Bitcoin wallet in your everyday life with your
mobile or you can have a wallet only for online payments on your
computer. In any case, choosing your wallet can be done in a minute.
Choose your wallet
3. Get Bitcoin
You can get Bitcoin by accepting it as a payment for goods and services. There are also several ways you can buy Bitcoin.
Buy Bitcoin
4. Spend Bitcoin
There is a growing number of services and merchants accepting
Bitcoin all over the world. You can use Bitcoin to pay them and rate
your experience to help honest businesses to gain more visibility.
Find merchants and products
How to accept Bitcoin
1. Inform yourself
Bitcoin does not require merchants to change their habits.
However, Bitcoin is different than what you know and use every day.
Before you start using Bitcoin, there are a few things that you need to
know in order to use it securely and avoid common pitfalls.
Read more
2. Processing payments
You can process payments and invoices by yourself or you can use
merchant services and deposit money in your local currency or bitcoins.
Most point of sales businesses use a tablet or a mobile phone to let
customers pay with their mobile phones.
Find merchant services
3. Accounting and taxes
Merchants often deposit and display prices in their local
currency. In other cases, Bitcoin works similarly to a foreign currency.
To get appropriate guidance regarding tax compliance for your own
jurisdiction, you should contact a qualified accountant.
Read more
4. Gaining visibility
There is a growing number of users searching for ways to spend
their bitcoins. You can submit your business in online directories to
help them easily find you. You can also display the Bitcoin logo on your website or your brick and mortar business.
-
By
 Bitcoin
Bitcoin - 2 comments
- 0 likes
- Like
- Share
-
By
-
Bitcoin is a very secure and inexpensive way to handle payments.
Choose your own fees
There is no fee to receive bitcoins, and many wallets let you control
how large a fee to pay when spending. Most wallets have reasonable
default fees, and higher fees can encourage faster confirmation
of your transactions. Fees are unrelated to the amount transferred, so
it's possible to send 100,000 bitcoins for the same fee it costs to send
1 bitcoin.
Protection against fraud
Any business that accepts credit cards or PayPal knows the problem of
payments that are later reversed. Chargeback frauds result in limited
market reach and increased prices, which in turn penalizes customers.
Bitcoin payments are irreversible and secure, meaning that the cost of
fraud is no longer pushed onto the shoulders of the merchants.
Fast international payments
Sending bitcoins across borders is as easy as sending them across the
street. There are no banks to make you wait three business days, no
extra fees for making an international transfer, and no special
limitations on the minimum or maximum amount you can send.
No PCI compliance required
Accepting credit cards online typically requires extensive security
checks in order to comply with the PCI standard. Bitcoin still requires
you to secure your wallet
and your payment requests. However, you do not carry the costs and
responsibilities that come with processing sensitive information from
your customers like credit card numbers.
Get some free visibility
Bitcoin is an emerging market of new customers who are searching for
ways to spend their bitcoins. Accepting them is a good way to get new
customers and give your business some new visibility. Accepting a new
payment method has often shown to be a clever practice for online
businesses.
Multi-signature
Bitcoin also includes a multi-signature feature which allows bitcoins
to be spent only if a subset of a group of people authorize the
transaction. This can be used by a board of directors to prevent any
member to make expenditures without enough consent from other members,
as well as to track which members allowed each payment.
Accounting transparency
Many organizations are required to produce accounting documents about
their activity. Using Bitcoin allows you to offer the highest level of
transparency since you can provide information your members can use to
verify your balances and transactions. Non-profit organizations can also
allow the public to see how much they receive in donations.
-
Bitcoin is the simplest way to exchange money at very low cost.
Mobile payments made easy
Bitcoin on mobiles allows you to pay with a simple two step
scan-and-pay. No need to sign up, swipe your card, type a PIN, or sign
anything. All you need to receive Bitcoin payments is to display the QR
code in your Bitcoin wallet app and let your friend scan your mobile, or
touch the two phones together (using NFC radio technology).
Security and control over your money
Bitcoin transactions are secured by military grade cryptography.
Nobody can charge you money or make a payment on your behalf. So long as
you take the required steps to protect your wallet, Bitcoin can give you control over your money and a strong level of protection against many types of fraud.
Works everywhere, anytime
Just like with email, you don't need to ask your family to use the
same software or the same service providers. Just let them stick to
their own favorites. No problem there; they are all compatible as they
use the same open technology. The Bitcoin network never sleeps, even on
holidays!
Fast international payments
Sending bitcoins across borders is as easy as sending them across the
street. There are no banks to make you wait three business days, no
extra fees for making an international transfer, and no special
limitations on the minimum or maximum amount you can send.
Choose your own fees
There is no fee to receive bitcoins, and many wallets let you control
how large a fee to pay when spending. Most wallets have reasonable
default fees, and higher fees can encourage faster confirmation
of your transactions. Fees are unrelated to the amount transferred, so
it's possible to send 100,000 bitcoins for the same fee it costs to send
1 bitcoin.
Protect your identity
With Bitcoin, there is no credit card number that some malicious
actor can collect in order to impersonate you. In fact, it is even
possible to send a payment without revealing your identity, almost like
with physical money. You should however take note that some effort can
be required to protect your privacy.
-
By
 Bitcoin
Bitcoin - 2 comments
- 0 likes
- Like
- Share
-
By
-
On 18 August 2008, the domain name "bitcoin.org" was registered.[27] In November that year, a link to a paper authored by Satoshi Nakamoto titled Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System[15] was posted to a cryptography mailing list.
[27]Nakamoto implemented the bitcoin software as open source code and released it in January 2009.[28][11] The identity of Nakamoto remains unknown.[10]In January 2009, the bitcoin network came into existence after Satoshi Nakamoto mined the first ever block on the chain, known as the genesis block, for a reward of 50 bitcoins.[29][30] Embedded in the coinbase of this block was the following text:The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks.[11]
This note has been interpreted as both a timestamp of the genesis date and a derisive comment on the instability caused by fractional-reserve banking.[31]One of the first supporters, adopters, and contributors to bitcoin was the receiver of the first bitcoin transaction, programmer Hal Finney.
Finney downloaded the bitcoin software the day it was released, and received 10 bitcoins from Nakamoto in the world's first bitcoin transaction.[32][33] Other early supporters were Wei Dai, creator of bitcoin predecessor b-money, and Nick Szabo, creator of bitcoin predecessor bit gold.
[34]In the early days, Nakamoto is estimated to have mined 1 million bitcoins.[35] In 2010, Nakamoto handed the network alert key and control of the Bitcoin Core code repository over to Gavin Andresen, who later became lead developer at the Bitcoin Foundation.[36][37] Nakamoto subsequently disappeared from any involvement in bitcoin.
[38] Andresen stated he then sought to decentralize control, saying: "As soon as Satoshi stepped back and threw the project onto my shoulders, one of the first things I did was try to decentralize that. So, if I get hit by a bus, it would be clear that the project would go on."[38] This left opportunity for controversy to develop over the future development path of bitcoin.
[39]The value of the first bitcoin transactions were negotiated by individuals on the bitcointalk forums with one notable transaction of 10,000 BTC used to indirectly purchase two pizzas delivered by Papa John's.[29]
On 6 August 2010, a major vulnerability in the bitcoin protocol was spotted.
Transactions were not properly verified before they were included in the blockchain, which let users bypass bitcoin's economic restrictions and create an indefinite number of bitcoins.[40][41] On 15 August, the vulnerability was exploited; over 184 billion bitcoins were generated in a single transaction, and sent to two addresses on the network.
Within hours, the transaction was spotted and erased from the transaction log after the bug was fixed and the network forked to an updated version of the bitcoin protocol.[42][40][41]On 1 August 2017, a hard fork of bitcoin was created, known as Bitcoin Cash. Bitcoin Cash has a larger blocksize limit and had an identical blockchain at the time of fork. [43][44][45]
Continue reading on Wikipedia : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bitcoin
-
By
 Bitcoin
Bitcoin - 2 comments
- 0 likes
- Like
- Share
-
By



























